Dr Z Kanili Jimo
CIHSR
What is Cervix?
The cervix is the lower part of the womb also known as uterine cervix. The cervix connects the body of the uterus to the vagina (birth canal). The cervix is about 2-3 centimetres in length.
Some frequently asked questions on cervical cancer
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix
Is cervical cancer common in India?
Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among Indian women. One woman dies of cervical cancer every 8 minutes in India.
What are the risk Factors for Cervical Cancer?
Risk factors for cervical cancer include:
• Human papillomaviruses (HPV) infection: Infection by the human papillomaviruses (HPV) is the most important risk factor for cervical cancer. Not all types of HPV cause cervical cancer. Some of them cause genital warts, but other types may not cause any infections
• Many sexual partners. The greater your number of sexual partners and the greater your partner's number of sexual partners, the greater your chance of acquiring HPV and hence cervical cancer.
• Early sexual activity. Becoming sexually active at a young age (especially younger than 18 years old) increases your risk of HPV.
• Becoming pregnancy many times. Increasing number of pregnancy has been correlated with cervical cancer risk
• Co-infection with HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). Women living with HIV are 6 times more likely to develop cervical cancer compared to women without HIV.
• Smoking. Women who smoke are 2 times more likely to develop cervical cancer compared to women who don't smoke.
• Lack of screening /inadequatescreening: the greatest risk for cervical cancer is the lack of regular Pap smear screening.
• Long-term use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
• Other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Having other STIs such as Chlamydia, gonorrhoea, herpes and HIV/AIDS increases your risk of HPV.
• Having a family history of cervical cancer. Cervical cancer may run in some families. If your mother or sister had cervical cancer, your chances of developing the disease are higher than if no one in the family had it.
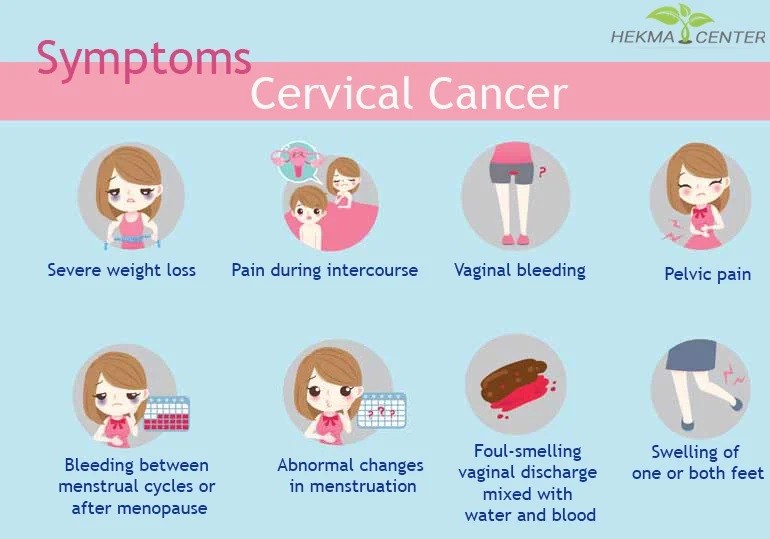
How will I know if I am suffering from cervical cancer?
In Early-stage cervical cancer you may have no signs or symptoms, however in more-advanced cervical cancer you may experience:
• Vaginal bleeding after sex
• Vaginal bleeding in between periods
• Vaginal bleeding after menopause (permanent stoppage of menses)
• Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and foul smelling
• Pain during intercourse
• Lower abdominal pain
Is there a test for cervical cancer?
Yes. A Pap test (also called a "Pap smear") is used to screen for cervical cancer. Doctors sometimes also do a test for a human papillomavirus(HPV). If cervical cancer is suspected, your doctor may use:
• A special magnifying instrument (Colposcope) to check for abnormal cells.
• Punch biopsy to pinch off small samples of cervical tissue.
How is cervical cancer treated?
Cervical cancer treatment depends on several factors such as the stage of your cancer, your age, and other health problems. Your treatment will also depend on whether you might want to get pregnant in the future. The treatment options include surgery, radiation and chemotherapy
Is cervical cancer curable?
Cervical cancer can be cured if diagnosed at an early stage and treated promptly.
At what stage is carcinoma cervix curable?
With proper treatment, cervical cancer is potentially curable from stages 1 through 4A. Stage 4B is considered incurable. However, a percentage of people live for many years, even at this stage.
How quickly does cervical cancer progress from one stage to the next?
Cervical cancer develops slowly. It can take years before it progresses from one stage to the next. That's why regular checkups and testing, such as Pap smears, are so important.
Is supportive (palliative) care helpful in cervical cancer?
Palliative care is provided by a team of doctors, nurses and other specially trained professionals. Palliative care teams aim to improve the quality of life for people with cancer and their families. When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer.
Is cervical cancer preventable?
Yes, cervical cancer is a preventable disease.
How is cervical cancer preventable?
Cervical cancer has a well-defined, long pre-malignant (pre-cancerous) phase which can be detected and prevented by regular screening tests and follow up. Unfortunately, most women in India are not aware about the screening
How do I prevent cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer risks can be prevented by:
• Routine screening tests with Regular Pap smear tests to detect the cancerous conditions of the cervix. Most medical organizations suggest beginning routine Pap tests at age 21 and repeating them every few years.
• HPV vaccine. Receiving a vaccination to prevent HPV infection may reduce your risk of cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers. Ask your doctor whether an HPV vaccine is appropriate for you. Vaccination against HPV can be given from 9 to 45 years of age. Vaccine is effective if administered before becoming sexually active.
• Practice safe sex. Reduce your risk of cervical cancer by taking measures to prevent sexually transmitted infections, such as using a condom every time you have sex and limiting the number of sexual partners you have.
• Don't smoke. If you don't smoke, don't start. If you do smoke, talk to your doctor about strategies to help you quit.
Can Cervical Cancer Be Found Early?
The best way to find cervical cancer early is to have regular screening tests. The tests for cervical cancer screening are Pap test and the HPV test. Regular screening has been shown to prevent cervical cancers and save lives. The most important thing to remember is to get screened regularly.
Five key messages
1. Cervical cancer is a disease that can be prevented.
2. There are tests to detect early changes in the cervix (known as pre-cancers) that may lead to cancer if not treated.
3. There are safe and effective treatments for these pre cancers
4. All women aged 30–65 years should be screened for cervical cancer at least once.
5. There is a vaccine for girls that can help prevent cervical cancer.
The writer is Consultant , MS (Obstetrics & Gynaecology), Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, CIHSR





