Dr Leishiwon Kumrah
Ageing can have various effects on the skin, leading to changes in its appearance, texture, and function. The process of skin ageing is influenced by both intrinsic (internal) and extrinsic (external) factors. Here are some key aspects of ageing and the skin:
1. Intrinsic Ageing:
a. Genetic Factors: The natural ageing process is determined in part by genetics. Some people may age more gracefully or show fewer signs of ageing due to their genetic makeup.
b. Cellular Changes: As people age, the skin undergoes intrinsic changes at the cellular level. The rate of cell turnover slows down, leading to a decrease in the production of essential proteins like collagen and elastin.
c. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during menopause in women, can contribute to changes in skin structure and hydration.
2. Extrinsic Ageing:
a. UV Radiation: Sun exposure is a major contributor to premature ageing. UV rays from the sun can damage collagen and elastin fibres, leading to wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin.

b. Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, harsh weather conditions, and toxins can accelerate the ageing process.
c. Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as smoking, poor nutrition, and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact the skin's health and contribute to premature ageing.
3. Effects on the Skin:
a. Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Reduction in collagen and elastin production can result in the development of wrinkles and fine lines.
b. Loss of Elasticity: As the skin loses its elasticity, it may sag and appear less firm.
c. Dryness and Thinning: A decrease in oil production and skin thickness can lead to dryness and thinning of the skin.
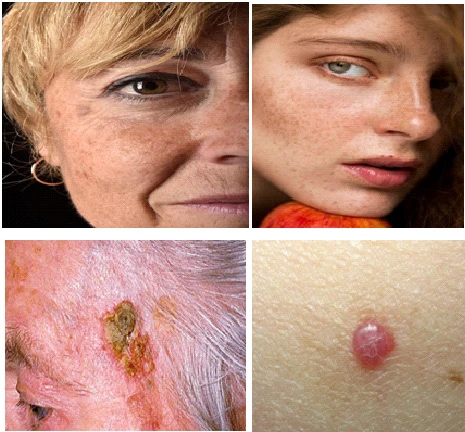
d. Uneven Pigmentation: Age spots, sun spots, and changes in pigmentation may occur due to sun damage and other factors.
e. Skin coloured to darker brown soft papules are seen mainly over the neck, axilla and below the breast.
f. Tan to Brown spots with greasy surfaces, small to large are seen mainly over the face, neck and trunk.
g. Pinkish or Reddish spots known as cherry angiomas also appear as we grow older and this is also seen mostly in the trunk and limbs.
4. Preventive Measures:
a. Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen with a high SPF can protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
b. Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hydration supports overall skin health.

c. Skincare Routine: Using skincare products that contain antioxidants, retinoids, and moisturizers can help minimize the effects of ageing.
d. Avoiding Harmful Habits: Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and avoiding excessive stress can contribute to healthier skin.
5. Treatment Options:
a. Topical Treatments: Retinoids, antioxidants, and moisturizers can help improve the appearance of ageing skin.
b. Cosmetic Procedures: Various cosmetic procedures, such as laser therapy, chemical peels, and injectables like Botox, can address specific signs of ageing.
c. Dermatological Interventions: Dermatologists may recommend specific treatments based on individual skin concerns.
While ageing is a natural process, adopting a proactive approach to skincare and making healthy lifestyle choices can help maintain skin health and minimize the visible effects of ageing. It's important to consult with skincare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options based on individual skin types and concerns.
(The writer is Senior Consultant and HOD Department of Dermatology, Venereology, Leprology & Cosmetology, Christian Institute of Health Sciences and Research CIHSR)





